NEW IN CONTINUUM 2021, the BCC+ Diffusion filter creates atmosphere by reducing contrast while creating a glow around highlights or shadows using an extensive texture library.

Photo by Marina Vitale on Unsplash
Presets and the FX Editor
To select from a selection of factory installed and user-generated presets, open the FX Editor interface and pick one from the Presets window.
Filter Parameters
Diffusion
Blend: Determines the blend mode to be used to create the diffusion effect.
- Add: The diffusion is added to your image.
- Screen: The diffusion is combined with the image using a Screen blend mode. This looks kind of like the Add blend mode, but highlights are retained.
Brightness: Sets the intensity of the diffusion.
Blur: Sets the softness of the diffusion.
Color: The Color parameter sets the color of the diffusion through the use of a standard color picker. The default color is white.
Color Correction
- Hue: Rotates the hue of the image.
- Saturation: Adjusts the saturation of the image. Positive values saturate, negative values desaturate.
- Brightness: Adjusts the brightness of the image. Positive values brighten, negative values darken.
- Contrast: Adjusts the contrast of the image. Positive values increase contrast, negative values decrease contrast.
- Gamma: Adjusts the gamma of the image. The gamma adjustment leaves the white and black points the same and only modifies the values in-between. Positive values lighten the midtones, negative values darken the midtones.
- Temperature: Sets the color of the image to be either warmer or cooler. Dragging the slider to the right makes the image cooler (bluer) and dragging the slider to the left makes the image warmer (redder).
- Cyan/Magenta: Adds either Cyan or Magenta to the image. Dragging the slider to the right makes the image more magenta and dragging the slider to the left makes the image more cyan.
- Red: Adds or subtracts red from the image.
- Green: Adds or subtracts green from the image.
- Blue: Adds or subtracts blue from the image.
Texture
Texture: Selects the texture which will be used to add diffusion to the image.
Blend: Textures can be used as the source of the diffusion as well as combined with a matte using a variety of Blend modes.
- Texture Only: Displays the texture source normally, without any blending.
- Add: The pixels of one image are added to another image
- Subtract: Looks at the color information in each channel and subtracts either the blend color from the base color or the base color from the blend color, depending on which has the greater brightness value. Blending with white inverts the base color values; blending with black produces no change.
- Multiply: Looks at the color information in each channel and multiplies the base color by the blend color. The result color is always a darker color. Multiplying any color with black produces black. Multiplying any color with white leaves the color unchanged.
- Screen: Looks at each images color information and multiplies the inverse of the two images. This looks kind of like the Add blend mode, but highlights are retained.
- Difference: Looks at the color information in each channel and subtracts either the blend color from the base color or the base color from the blend color, depending on which has the greater brightness value. Blending with white inverts the base color values; blending with black produces no change.
- Darken: Looks at the color information in each channel and selects the base or blend color—whichever is darker—as the result color. Pixels lighter than the blend color are replaced, and pixels darker than the blend color do not change.
- Lighten: Looks at the color information in each channel and selects the base or blend color—whichever is lighter—as the result color. Pixels darker than the blend color are replaced, and pixels lighter than the blend color do not change.
The Multiply blend mode is ideal for combining the texture source with the matte because it only puts the texture source within the areas of the matte.
Transform
Transform your light pattern using Position, Scale, Rotate, Corner-Pin, Shear and Crop controls.
Crop
The image can be cropped by adjusting the various Crop parameters.
- Top: Crops the image from the top down.
- Bottom: Crops the image from the bottom up.
- Left: Crops the image from left to right.
- Right: Crops the image from right to left.
Corner Pin
The image can be corner pinned by adjusting the Corner Pin sliders as well as dragging the four points on the corners of the screen.
Note: You may need to zoom the image out a bit to see the corner points. In addition, to see and adjust the corner points in After Effects, make sure that the effect title in the Effect Controls window is highlighted. For Final Cut Pro, you must activate the cross hair icon next to the corner position parameters to see and adjust the corner points on the screen.
- Upper-Left: Controls the X and Y position of the Upper Left Point.
- Upper-Right: Controls the X and Y position of the Upper Right Point.
- Lower-Right: Controls the X and Y position of the Lower Right Point.
- Lower-Left: Controls the X and Y position of the Lower Left Point.
Position
Position can be adjusted by clicking and dragging an on-screen control in the center of the image.
- Position X: The horizontal position.
- Position Y: The vertical position.
Note: For Final Cut Pro, you must activate the cross hair icon next to the Position parameter.
Scale
The scale of the image can be changed by adjusting the vertical and horizontal scale parameters.
- Scale X: The horizontal scale.
- Scale Y: The vertical scale.
- Gang Scale: The Scale X and Scale Y slider values can be ganged together. When enabled, the scale parameter will not display individual X and Y parameters.
Rotate
In addition to the standard position and scale controls, you can rotate. Positive values rotate clockwise and negative values rotate counter-clockwise.
Shear
In addition to the standard position, scale and rotation controls, you can shear, or skew, the image.
- Shear X: Skews left and right.
- Shear Y: Skews up and down.
Anchor
Anchor points determine the position along the X and Y axis upon which the position, rotation, scaling and shearing occur.
- Anchor X: Defines the point on the X axis around which position, rotation, scaling or shearing takes place.
- Anchor Y: Defines the point on the Y axis around which position, rotation, scaling or shearing takes place.
Filter
You can choose the filtering method when applying a transform to the image. Mitchell is the default, however a number of additional filtering options are available.
- Triangle: The Triangle filter is not the highest quality, but fine for scaled images.
- Quadratic: Quadratic is like triangle, but more blur with fewer artifacts. It offers a good compromise between speed and quality.
- Cubic: Cubic is the default filter in Photoshop. It produces better results with continuous tone images, but is slower than Quadratic. If the image contains fine details, the result may be blurrier than desired.
- Catmull-Rom: This produces good results with continuous tone images which are scaled down, producing sharp results with fine detailed images.
- Gaussian: Gaussian lacks in sharpness, but is good with ringing and aliasing.
- Mitchell: A good balance between sharpness and ringing, Mitchell is a good choice when scaling up.
- Sinc: Keeps small details when scaling down with good aliasing.
Matte
A matte can be used to create the diffusion effect.
Position: Pinpoints the color values to be used in the matte. For a luminance matte, a Position value of 100 would make a white matte of the highlights and a value of 0 would make a white matte of the shadows. In the flower image below, look at how the matte varies for different Position values in a red extraction. When the Position is at a value of 100, the red flowers are shown as white in the matte.

When the Position is moved to 50, the red flowers turn black.
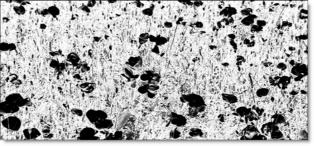
Range: Increases or decreases the range of values in the matte. A low Range value indicates a narrow range of values. A high Range value indicates a large range of values included in the matte.
Blur: The matte is blurred by a quality blur.
Working with The Filter
- Apply BCC+ Diffusion from the BCC Optical Diffusion unit category.
- Click the BCC FX Editor button to launch the FX Editor user interface.
- Try out some of the presets. Each preset uses a different texture to create the diffusion effect.
- Adjust the Diffusion > Brightness parameter to control the amount of diffusion added to the image.You can either use the texture by itself or combine it with a matte using one of the Texture > Blend modes. The areas that are white in the matte are the areas where diffusion will be introduced.
- Combine the texture with a matte by changing Texture > Blend from Texture Only to Multiply.I like the Multiply blend mode because it only adds the texture in the areas of the matte.
- Change your View to Matte to see the matte values.The areas that are white in the matte are the areas where diffusion will be introduced. The location of the diffusion within the scene can be adjusted by modifying the Matte > Position and Range parameters.
- Change the Matte > Position parameter if you want to add diffusion to different areas of the image.
- Adjust the Matte > Range slider to increase or decrease the image areas affected by the diffusion.
- Change your View to Output to see the filtered image.
- Adjust the position of the texture by clicking and dragging the center image point to the desired location.
- You can also use the Texture > Transform controls to transform the texture.
- Adjust the Diffusion > Brightness, Blur and Color of the diffusion to your liking.
- Click the Apply button to return to the host application
The values of the parameter adjustments in the FX Editor user interface are transferred to your host application.