Overview
The Spline Primitive and Spline Object media types allow you to create and edit vector-based media within Title Studio. You can also import vector-based images from other applications and then edit them within Title Studio, or convert text characters to spline objects so that you can edit and animate them. The Spline Object media type offers many options for drawing custom splines, while Spline Primitive allows you to quickly create objects in a number of preset shapes. Both media types are available in all shape tracks.
Working With the Spline Primitive Media Type
The Spline Primitive media type allows you to quickly create spline objects in basic shapes, including rectangles, circles, stars, arrows, hearts, and medallions. A number of Control Window parameters on the Media Track offer control over the stroke and fill, as well as the shape and size of the path itself. Once you create a Spline Primitive you can convert it to a Spline object and use the Pen tool to edit the shape.
Creating Spline Primitives
There are three ways to create a Spline Primitive: From the menu, the project window or with a keyboard shortcut. As with all media, make sure that you have selected the apropropriate scene container before creating a new Spline Primitive.
You can create a spline primitive:
- From the Track Menu. Select Track —> New Media —-> Spline Primitive.
- From the Project Window. Select the Add New Media drop down menu. Then select Spline Primitive
- Enter the keyboard shortcut: Ctrl+Alt+A
Working with the Control Window
To change the shape, fill, border, shadow and other aspects of your Spline Primitive, you will need to select the track media. When you select this track level, the available parameters in the Control Window allow you to modify the overall shape and look of your Spline Primitive. For more information on working with tracks, please refer to the section on Understanding Track Order.
Working with the Shape Tab
The Shape tab determines the shape of the spline primitive and allows you to adjust the shape and size of the spline.
Available shapes include:
- Rectangle
- Wedge
- Oval
- Arrow
- Star
- Medalion
- Heart
- Grid
- Line
Click one of the Shapes to create the coresponding spline primitive. Each primitive shape has its own parameters which are described in detail in the following sections.
Tip: Since Grid or Line shapes do not have fill parameters, selecting them disables this parameter. Remember to re-enable Fill if you wish to switch back to another shape.
Rectangle Spline Primitive Shape
Rectangle creates a rectangular or square-shaped spline. When you click the Rectangle tab, the following controls are available in the Shape tab:
- Left, Top, Right, and Bottom control the positions of the corners of the rectangle. These values are scaled as percentages of the width and height of the Composite window.
- Corner Size adjusts the size of the rectangle’s corners.

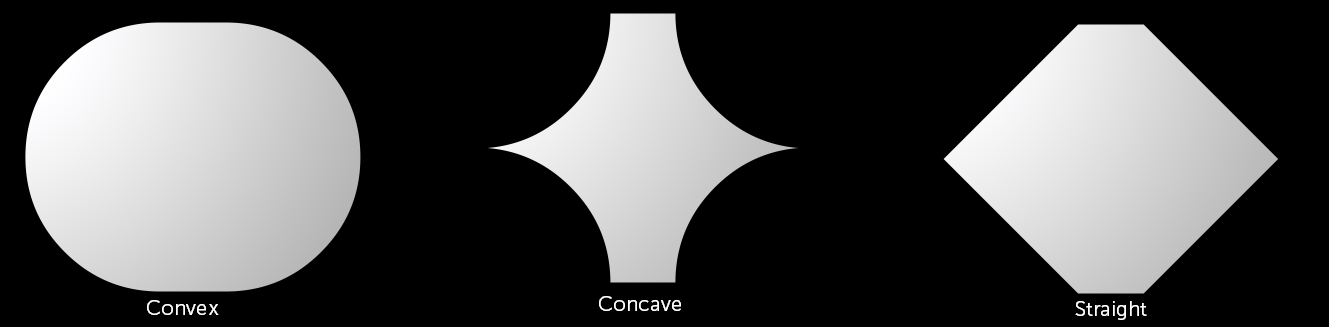
- Corner Type sets the shape of the rectangle’s corners.
- Convex produces corners that curve inward.
- Concave produces corners that curve outward.
- Straight produces corners that are straight lines.
Wedge Spline Primitive Shape
Wedge creates circular or wedge-shaped splines. When you click the Wedge tab, the following controls are available in the Shape tab:
- Start Angle sets the location of the starting edge of the wedge. Increasing this value moves the starting edge around the Z axis.
- Arc Angle specifies the distance between the starting and ending edges of the wedge, or the length of the arc which forms the outer edge of the wedge.
Oval Spline Primitive Shape
Oval creates oval splines. Unlike other primitives, Ovals have no parameter controls in the Shape tab.
Arrow Spline Primitive Shape
Arrow creates arrow-shaped splines. When you click the Arrow tab, the following controls appear in the Shape tab:
- The Arrow Type menu determines which way the arrow points. Choose Up, Down, Left, or Right.
Star Spline Primitive Shape
Star creates star-shaped splines. When you click the Star tab, the following controls are available in the Shape tab:
- Points sets the number of points in the star. Higher values produce more points, while lower values produce fewer points.
- Length sets the length of each point in the star. Higher values produce longer points, while lower values produce shorter points.
Medallion Spline Primitive Shape
Medallion creates a a medallion-shaped spline. The medallion shape is similar to a star, but with a greater number of shorter points. In addition, the medallion is stretched horizontally. When you click the Medallion tab, the following controls are available in the Shape tab:
- Points adjusts the number of points in the medallion. Higher values produce more points, while lower values produce fewer points.
- Length sets the length of each point in the medallion. Higher values produce longer points, while lower values produce shorter points.
TIP: Star and Medallion Primitives share Points Parameters. This means that changes to the point value for a Star Primitive will remain if you change it to a Medallion. This allows you to compare the two without having to reset the points every time.
Heart Spline Primitive Shape
Heart produces a heart-shaped spline. When you click the Heart tab, the following controls are available in the Shape tab:
- Roundness adjusts the shape of the point at bottom of the heart. Lower values produce a more rounded point, while higher values produce a narrower point.
Grid Spline Primitive Shape
Grid produces a grid-shaped spline. When you click the Grid tab, the following controls appear in the Shape tab:
- Columns and Rows set the number of grid lines along the X and Y axes, respectively. By default the grid includes eight columns and six rows.
- Spacing X and Spacing Y scale the distance between lines along the X and Y axes, scaled as percentages of the grid’s original width or height. To scale the size of entire grid, use the Scale parameter in the Position tab.
- Shift X and Shift Y position the grid lines on the X and Y axis respectively. The values are relative: they indicate the number of pixels that the line is offset from its starting position.
- Selecting the Hide Top, Hide Bottom, Hide Left and Hide Right checkboxes hide the corresponding extreme lines.
- Skew X and Skew Y distort the lines along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively.
- Start X and Start Y allow you to set the starting position of the lines along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively. This allows you to create lines that are shorter than full length or lines that animate.
- End X and End Y set the ending position of the lines along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively. This allows you to create lines that are shorter than full length or animate lines.
TIP: When you work with the Grid spline primitive, the controls in the Fill tab have no affect.
Line Spline Primitive Shape
Line produces a line-shaped spline. When you click the Line tab, the following controls appear in the Shape tab:
- Start X and Start Y allow you to set the starting position of the line along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively.
- End X and End Y set the ending position of the line along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively.
TIP: Use the Edge Width parameter in the Border tab to set the width of the line.
TIP: When you work with the Line spline primitive, the controls in the Fill tab have no affect. Lines cannot be filled.
REMINDER: Since Grid or Line shapes do not have fill parameters, selecting them disables this parameter. Remember to re-enable Fill if you wish to switch back to another shape.
Working with the Fill Tab
The Fill tab sets the color and opacity of the spline shape.
- Select the Fill On checkbox to turn on the fill for the spline. Deselect this option to leave the spline unfilled. If this checkbox is deselected, the other parameters in this tab will have no affect.
- Fill Opacity determines the opacity of the fill. Higher values will result in a more opaque object.
- The Fill Type menu determines the type of fill applied to the spline.
- Choose Color to apply a solid color fill. When Fill Type is set to Color, Fill Color sets the color of the fill. Click the color chip to access the system color picker, or use the eyedropper to choose a color. You can also enter RGB values into the numerical fields associated with the color control and press Enter.
- Choose Gradient to apply a gradient fill. You can apply a custom gradient by clicking the Gradient Editor icon to open the Gradient Editor. You can also use the Style Palette to add a custom preset gradient. When you choose Gradient from the Fill Type menu and launch the Gradient Editor you can adjust many of the same parameters found in the Color Stops tab for the Gradient media type, with one exception: You cannot animate gradients that are added via the Fill Type menu.
Working with the Border Tab
The Border tab lets you apply up to five different border styles to the edge of the spline primitive. The parameters in this tab can be used to create beveled or glowing shape effects.
To begin, click one of the numbered Border Style tabs to create a new border style. Select the checkbox next to the tab to apply the appropriate style. If the checkbox is not selected, the parameters in this tab have no affect. Each tab offers the following controls.
- The Edge Style menu controls the style of the border. Each style has its own controls, which are described in the following sections. The choices are Plain, Bevel and Radial.
- The Position menu sets the location of the border.
- Inside positions the border on the inside of the spline’s edges.
- Outside positions the border on the outside of the spline’s edges.
- Center centers the border over the spline’s edges, so half of the border is on the inside and half on the outside.
- Edge Color sets the color of the border. Click the color chip to access the system color picker, or use the eyedropper to choose a color from the screen. You can also enter RGB values into the numerical fields.
- Edge Width sets the width, in pixels, of the border applied to the spline.
- Edge Opacity adjusts the opacity of the border. A setting of 100 makes the border completely opaque, while a setting of 0 makes the border completely transparent.
Edge Style Plain Options
Plain creates a standard border effect. When Plain is chosen the following controls become available:
- Edge Softness softens the edge of the border. A value of 0 creates a border with a hard edge, and raising this value increasingly softens the border.
- Cap controls the shape of the ends of the border.
- Flat creates flat ends.
- Round adds a circular cap to the end of the stroke, which slightly lengthens the stroke and creates a rounded end.
- Square adds a square cap to the end of the stroke, which slightly lengthens the stroke and creates a flat end with square corners.
- Join menu determines the shape of the corners of the border.
- Round to create rounded corners
- Miter to create corners with sharp points
- Bevel to create clipped corners.
Edge Style Bevel Options:
Bevel creates a beveled border effect. When Bevel is chosen the following parameters become available:
- Highlight Color sets the color of the lightest parts of the bevel. Click the color chip to access the system color picker, or use the eyedropper to choose a color from the screen. You can also enter RGB values into the numerical fields.
- Shade Color sets the color of the darkest parts of the bevel. Click the color chip to access the system color picker, or use the eyedropper to choose a color from the screen. You can also enter RGB values into the numerical fields.
- Highlight Angle sets the angle between the highlights and the horizontal axis. Click the color chip to access the system color picker, or use the eyedropper to choose a color from the screen. You can also enter RGB values into the numerical fields.
Edge Style Radial Options
Radial creates a gradient border effect. When Radial is chosen the following parameters become available:
- Outside Color sets the color of the soft edges of the border.
- Radial Fade controls the opacity of the outer edge of the border. When Radial Fade is zero, the outer edge is opaque. Higher Radial Fade values increase the transparency of the edge, and at a value of 6, the outer edge is transparent.
- Edge Softness softens the edges of the glowing border. A value of 0 creates a border with a hard edge, and raising this value increasingly softens the border.
Animating the Border
You can animate the border by adjusting the various border parameters and setting a keyframe. Experiment with the various interpolation settings to achieve different effects.
- Border Begin and Border End adjust the percentage of the border that is visible at each frame in the timeline. These values are measured as a percentage of the complete border. For example, if Border Start is set to 0 and Border End is set to 50, the first half of the border is visible. If Border Start is set to 50 and Border End to 100, the second half of the border is visible.
- Use the Border Offset in conjunction with Border Begin and Border End to select a portion of the border and animate it.
Working with the Shadow Tab
The Shadow tab lets you apply up to five different shadows to the spline primitive shapes.
Click one of the numbered Shadow Style tabs to create a new shadow style. Select the checkbox next to the tab to apply the appropriate style to the selected spline. Each tab offers the following controls. The Shadow Type menu determines what type of shadows are created. • Drop Shadows fall a specified distance from the object. • Cast Shadows appear to fall on another object; therefore the appearance and shape of this type of shadow depends on the Shadow Distance that you set. • Solid Shadows simulate a 3D appearance by applying a gradient to a shadow. Solid shadows are useful if you want a three dimensional appearance but do not need to apply transformations that would reveal that the spline is actually 2D. For example, a rectangle with solid shadows will render more quickly than the 3D Extrusion shape. Color sets the color of the shadow. Click the color chip to access the system color picker, or use the eyedropper to choose a color from the screen. You can also enter RGB values into the numerical fields and press Enter. You can also apply colors from the Style Palette. For more information, see “Applying Color, Natural, Gradient or Extrusion Styles” on page 110. Distance sets the distance between the shadow and the spline object. Use a small value to offset the shadow slightly; use a larger value to create distinct shadows that appear to fall on another surface. Working with Spline Media 409 • • • • • Opacity sets the degree of opacity. A value of 100 makes the shadow completely opaque. Decreasing this value makes the shadow increasingly transparent. A value of 0 creates a completely transparent shadow. Softness softens the edges of the shadows, emulating the appearance of shadows cast by a diffuse light source. A value of 0 creates shadows with hard edges. Increasing this value softens the shadow edges. Angle sets the angle between the shadow and the horizontal axis of the spline object. When Shadow Type is set to Solid Shadows, Highlight Color sets the color of the highlighted areas of the shadow, and Shade Color sets the color of the shaded areas. Click the color chip to access the system color picker, or use the eyedropper to choose a color from the screen.
Working with the Layer Tab Boris Blue includes a tab for Shape and Container tracks which defines “layer” or bitmap parameters for that track. Once you create a Spline or Spline Primitive shape, you can use the parameters in the Layer tab to create a backdrop behind the spline. The backdrop does not create a track in the timeline, therefore these parameters are not animatable.
Background Color controls the color of the background layer. Click the color chip to access the system color picker or use the eyedropper to choose a color from the screen. You can also type RGB values into the numerical fields and press Enter. Background Opacity sets the opacity of the background layer and is scaled as a percentage. A setting of 0% makes the background completely transparent, whereas a setting of 100% makes the image completely opaque. By default this setting is at 0. When the Invert Alpha checkbox is selected, the background’s original alpha channel is inverted, making areas where the alpha channel is black (0) completely opaque and areas where the alpha channel is white (255) completely transparent. Size X and Size Y adjust the size of the background track along the horizontal and vertical axes respectively. The size is expressed in pixels. Selecting the Force Size checkbox sets the background size to the size of the Project.
Converting a Spline Primitive to a Spline Object Once you create a Spline Primitive you can convert it to a Spline Object to edit the shape. This is useful if you want to use the Primitive shape as a starting point. For example, use the Heart Spline Primitive shape then convert it to a Spline Object and use the Pen tool to create a broken heart. 1. Press the Media icon on a spline primitive track and choose Spline Object from the menu. 2. When you set a track’s media type to Spline Object, the Tool window opens automatically. You can also open the Tool window by choosing Window > Show Tool Window, or pressing Control–6.